
Adding a User to the Sudo Group Using Command Line By adding a user to the sudo group, you can grant them permission to perform administrative tasks without logging in as the root user. The sudo group is a special group that allows users to run commands as the root user. Method 1: Adding a User to the Sudo Group We’ll explain each method in detail, including the pros and cons of each, so you can choose the best approach for your needs. In this article, we’ll cover the three methods of adding a user to the sudoers list in Debian: What should I do if I make a mistake in the sudoers file?.What are the advantages of adding a user to sudoers with different privileges?.How do I add a user to sudoers using the GUI?.How do I add a user to sudoers using the command line?.What is the difference between adding a user to sudoers and the sudo group?.Who can add a user to sudoers in Debian?.
Add user to sudoers debian full#
Adding a User to the Sudoers List with Full Privileges.Adding a User to the Sudoers List with Limited Privileges.Method 3: Adding a User to the Sudoers List with Different Privileges.Editing the Sudoers File Using Command Line.Adding a User to the Sudo Group Using the GUI.
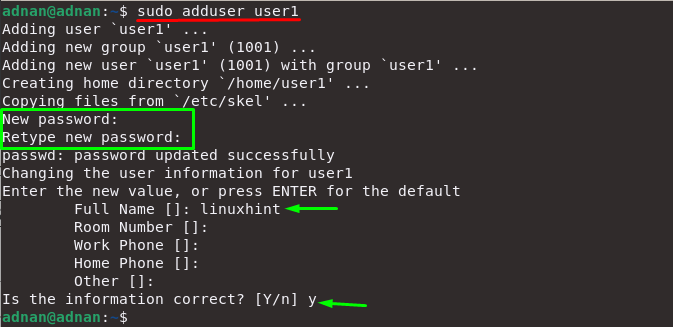
Adding a User to the Sudo Group Using Command Line.Method 1: Adding a User to the Sudo Group.

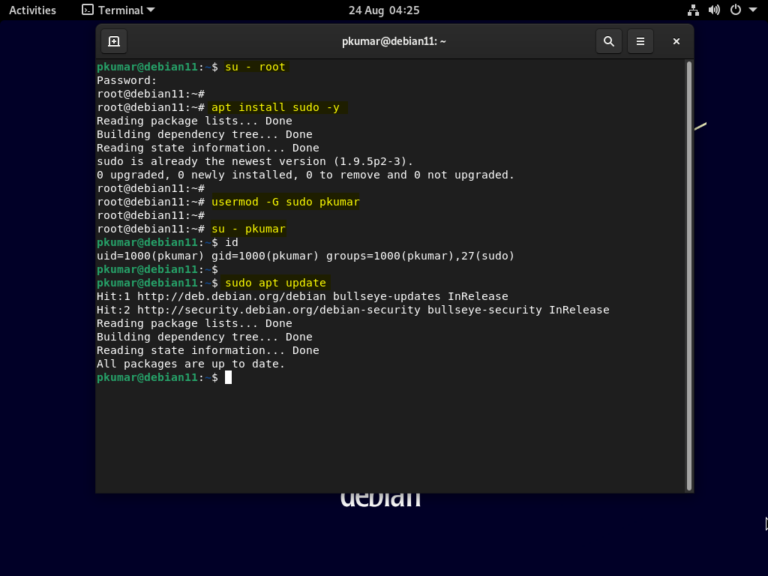
Now you have successfully created a new user on your Debian system with sudo privileges. Next, it’s time to grant “sudo” privileges to the user, for which you can run the following command: usermod -aG sudo (Even though you will later be using SSH to log into the server, it is still good practice to create this strong password.)
Add user to sudoers debian password#
However, you must create a strong password for the user. You can fill these out or optionally skip through them using your Enter key.

You will be prompted with several form fields. Once you are logged into the server, you can begin by creating the new user account with the adduser command: adduser Be sure to replace “” with your primary domain or dedicated IP address: ssh In order to accomplish this, you will have already added an SSH key to your server via the Account Management Panel. With the following commands you will effectively create a new sudo user on your system and be able to switch into that user.įirst, log into your system with the default root user. Allows your user to run root-level commands as needed, prepended with sudo.Makes user-specific actions easier to accomplish.Only pay for what you need with our scalable Cloud VPS Hosting.ĬentOS, Debian, or Ubuntu No Bloatware SSH and Root Access Reasons For Creating a Sudo User?Īs mentioned above, there are many reasons for creating a sudo user, but most significantly, creating a sudo user: If you don’t need cPanel, don't pay for it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
